The Resolve Tibet Act
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
- Context (IE): The United States Congress passed the Resolve Tibet Act, aiming to counter Chinese disinformation and promote dialogue for the resolution of the Tibet-China dispute.
Resolve Tibet Act
- The Resolve Tibet Act is the third major piece of U.S. legislation on Tibet, succeeding the Tibetan Policy Act (TPA) of 2002 and the Tibetan Policy and Support Act (TPSA) of 2020.
- Unlike its predecessors, the Resolve Tibet Act explicitly challenges China’s historical claims over Tibet and emphasises Tibetan self-determination and human rights.
Key Provisions
- Countering Disinformation: The Act authorises the use of funds to counter Chinese disinformation about Tibet’s history, people, and institutions, including the Dalai Lama.
- Promotion of Dialogue: It urges China to engage in direct, meaningful dialogue with the Dalai Lama or his representatives and elected Tibetan leaders without preconditions, aiming for a settlement.
- Human Rights and Self-Determination: The Act underscores Tibetans’ right to self-determination and human rights and China’s obligations under international covenants.
- For example: International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights and the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights.
- Cultural Preservation: It seeks to recognise and address Tibetans’ unique socio-cultural identity, including their historical, cultural, religious, and linguistic distinctiveness.
- Geographical Definition: The Act amends the TPA to define the geographical areas comprising the Tibetan Autonomous Region clearly.
Differences from Previous Legislation
- Tibetan Policy Act (TPA) of 2002: The TPA was cautious, recognising China’s claim over Tibet and encouraging dialogue without challenging China’s territorial assertions.
- It maintained that the Dalai Lama sought greater autonomy rather than independence.
- Tibetan Policy and Support Act (TPSA) of 2020: The TPSA pushed for dialogue without preconditions, emphasised Tibetan self-determination and encouraged international support for negotiations.
- Resolve Tibet Act of 2024: Unlike the TPA and TPSA, this Act directly challenges China’s historical claims over Tibet, promoting unconditioned dialogue.
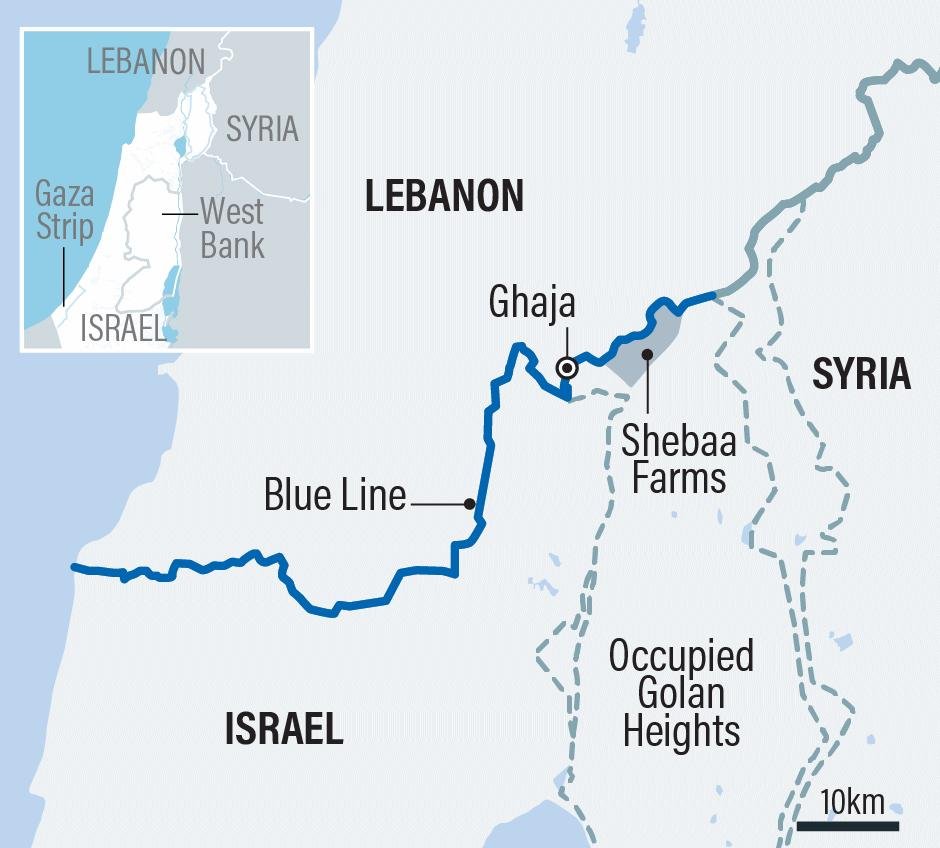
Implications for India
- Geopolitical Dynamics: The Act could influence India’s diplomatic relations with both China and the United States, necessitating a strategic balancing act.
- Support for Tibetan Refugees: India has a significant Tibetan refugee population, and the Act could affect international support and resources for these communities.
- Strategic Interests: India’s border security and regional stability could be impacted by the changing geopolitical landscape driven by this legislative measure.







![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](http://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)