Current Affairs for UPSC Civil Services Exam – April 21-22, 2024
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS1 – A&C – Religion} Bhagwan Mahavir Nirvan Mahotsav
- Context (PIB): On Mahaveer Jayanti, The Prime Minister inaugurated the 2550th Bhagwan Mahaveer Nirvan Mahotsav at Bharat Mandapam (New Delhi).
Kalyanaks
- Jains celebrate five Kalyanak’s (major life events) of every Tirthankar.
- These are Chyavana/Garbha (Conception) Kalyanak; Janma (Birth) Kalyanak; Diksha (Renunciation) Kalyanak; Kevaljnana (Omniscience) Kalyanak and Nirvana (Liberation/Ultimate Salvation) Kalyanak.
- The precise locations of all the five Kalyanaks of Bhagwan Mahavir are disputed, yet broadly agreed are:
- However, it is broadly agreed that Bhagwan Mahavir attained Nirvana at Pawapuri in Bihar.
To know more, visit > Jainism and Mahavir.
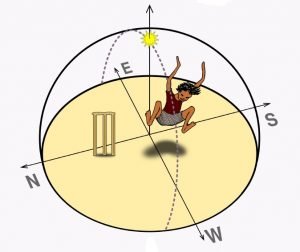
{GS1 – Geo – PG – Climatology} “Zero Shadow” Phenomenon
Context (TH): Zero Shadow Day was observed in Pondicheerry recently.
Conditions
- It occurs twice a year for places between +23.5 and -23.5 degrees latitude (i.e., the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn).
- Once between the December solstice (December 21 and 22) and the June solstice (June 20 and 21) and then between the June solstice and the December solstice.
- This phenomenon can never occur beyond the Tropics.
- The Sun should be nearly overhead at that particular latitude (Sun’s declination = Latitude)
Reasons behind zero shadow
- In such cases, sun rays will fall perpendicularly on a surface. In such a case, the shadow will be under it only and, thus, will not be seen.
{GS2 – IR – Australia} Australia releases National Defence Strategy 2024
- Context (TH): Australia released its new National Defence Strategy (NDS) 2024.
- The 2024 Integrated Investment Programme (IIP), which sets out Australia’s specific defence priorities, was also released.
- Australia will also continue to engage with partners outside the Indo-Pacific, including European nations.
- It notes that the risk of a crisis or conflict in the Taiwan Strait is increasing, as is the risk at other flashpoints, including the South and East China Seas.
- It observes that some of China’s initiatives in the Indo-Pacific also lack transparency regarding their purpose and scope.
Mentions of India in NDS 2024
- India-Australia have a Comprehensive Strategic Partnership aiming for Indo-Pacific stability.
- NDS 2024 also includes concern about India’s border dispute as a flashpoint for regional conflict.
- It observes the potential of tension and nuclear proliferation due to terrorism in the region.
- It acknowledges India’s role in the Indian Ocean region’s security and stability.
{GS2 – Social Sector – Health – Diseases} Diabetes
- Context (LM): Diabetes has been in the news due to the health concerns of Delhi CM.
- Diabetes, also called diabetes mellitus, is a chronic, progressive non-communicable disease (NCD) characterized by high levels of blood sugar (blood glucose) in the body.
- It occurs when:
- The pancreas does not produce enough insulin hormone that regulates blood sugar.
- The body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces.
- Hyperglycaemia, also called raised blood glucose, is a common effect of uncontrolled diabetes and over time leads to serious damage to the body’s systems, especially the nerves and blood vessels.
- About 422 million people worldwide have diabetes, the majority living in low-and middle-income countries, and 1.5 million deaths are directly attributed to diabetes each year.
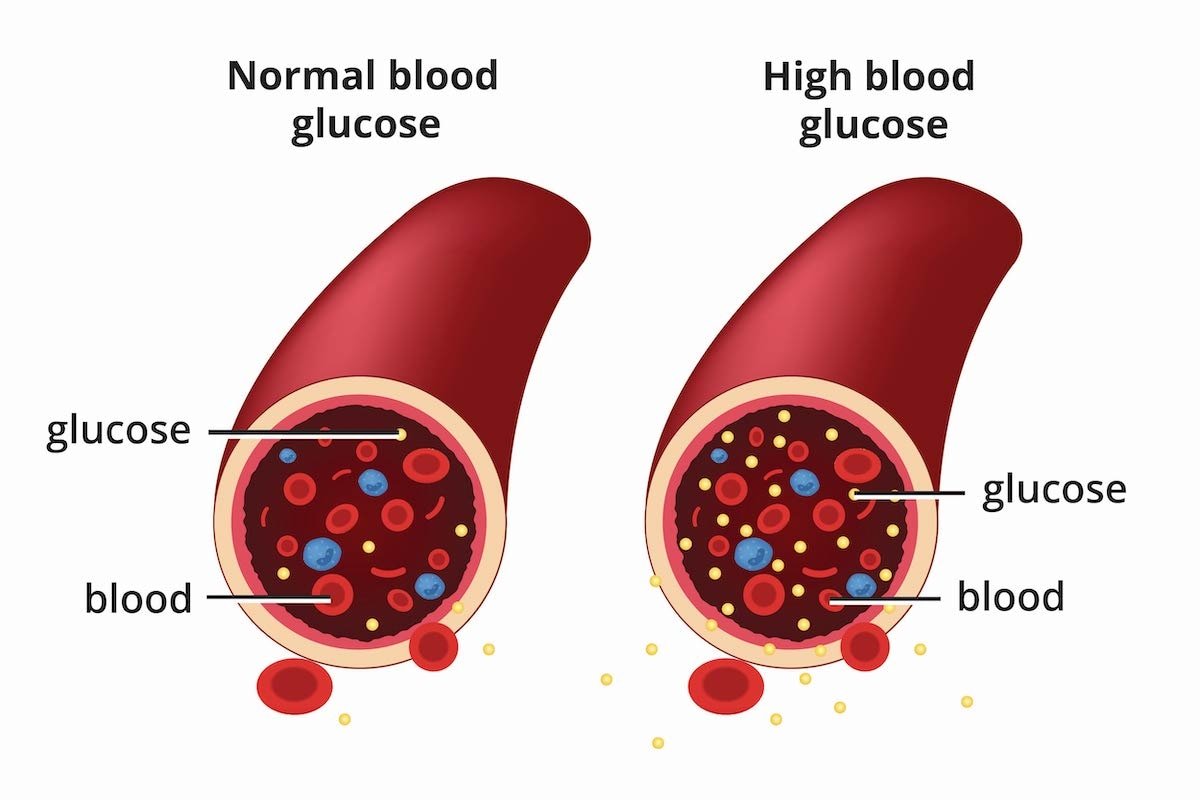
Types of Diabetes
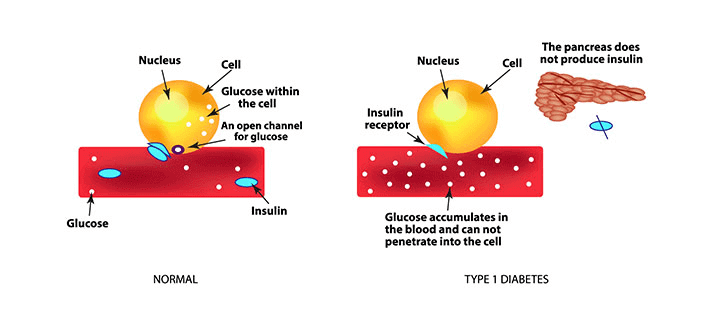
Type 1 Diabetes
- Type 1 diabetes (previously known as insulin-dependent, juvenile or childhood-onset) is caused by an autoimmune reaction (the body attacks itself by mistake). The immune system attacks and destroys cells in the pancreas, where insulin is made.
- This type of diabetes may be caused by a genetic predisposition. It could also be the result of faulty beta cells in the pancreas that normally produce insulin.
- People with type 1 diabetes may need daily insulin shots.
- Approximately 5-10% of the people who have diabetes have type 1. It is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, but it can develop at any age.
Type 1.5
- Type 1.5 diabetes is also known as latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA).
- It occurs during adulthood and sets in gradually like type 2 diabetes.
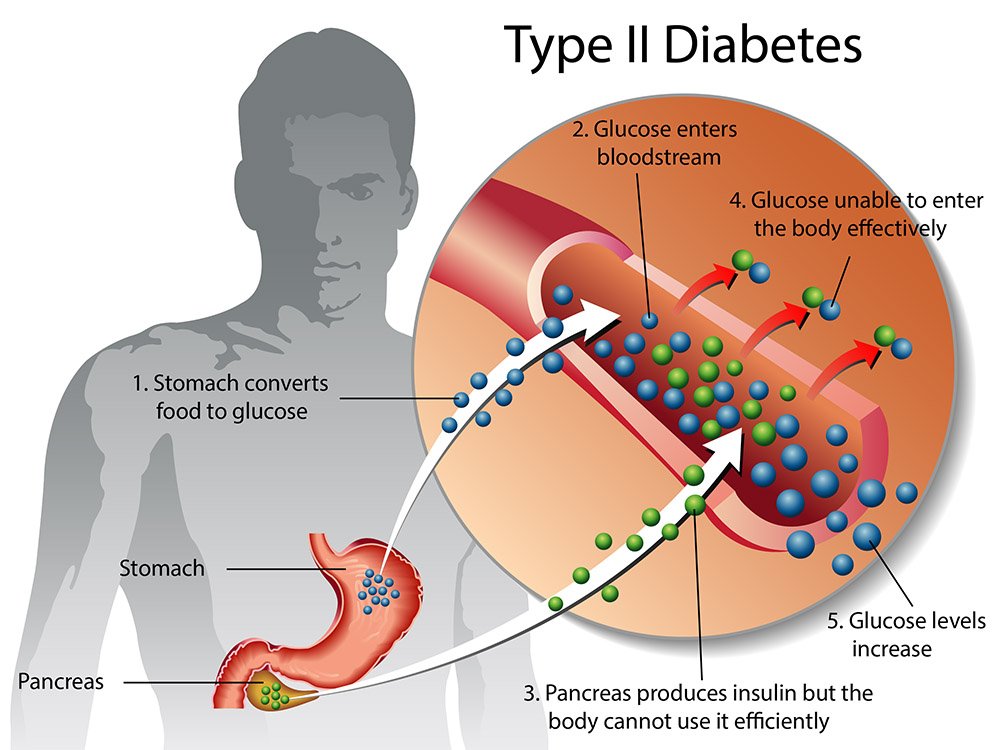
Type 2 Diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes affects how your body uses sugar (glucose) for energy. It stops the body from using insulin properly, which can lead to high levels of blood sugar if not treated.
- It used to be called adult-onset diabetes. About 90-95% of people with diabetes have type 2.
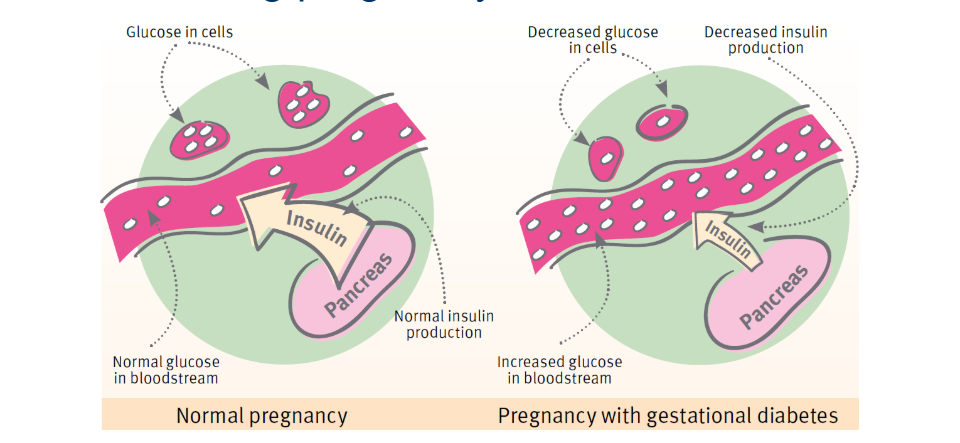
Gestational Diabetes
- Gestational diabetes is hyperglycaemia with blood glucose values above normal but below those diagnostic of diabetes.
- This type develops in some people during pregnancy.
Insulin
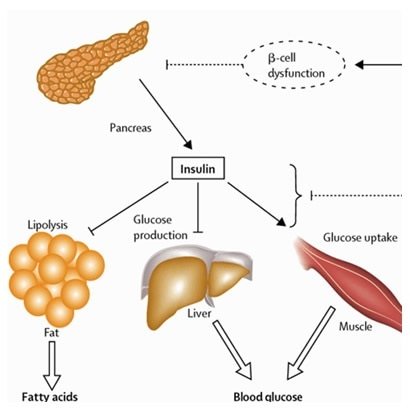
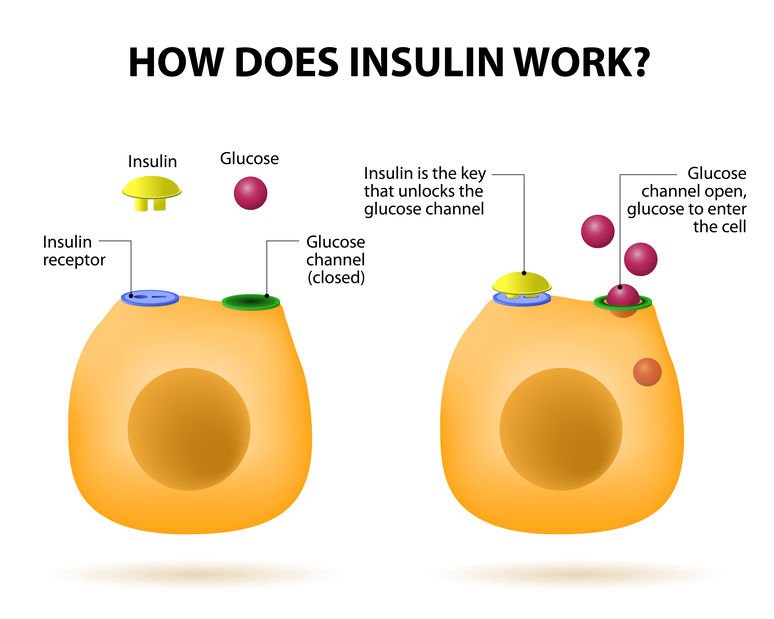
- The name insulin comes from the Latin ”insula” for “island” from the cells that produce the hormone in the pancreas. It is produced in the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas.
- It was discovered by Sir Frederick G Banting, Charles H Best and JJR Macleod in 1921.
- Insulin is synthesized in significant quantities only in beta cells in the pancreas.
- It is secreted primarily in response to elevated blood concentrations of glucose. Insulin thus can regulate blood glucose and the body senses and responds to rise in blood glucose by secreting insulin.
Functions of Insulin
- It causes the cells in the liver, muscle, and fat tissue to take up glucose from blood and convert it to glycogen that can be stored in the liver and muscles
- Insulin also prevents the utilization of fat as an energy source. In absence of insulin or in conditions where insulin is low, glucose is not taken up by body cells, and the body begins to use fat as an energy source.
- Insulin also controls other body systems and regulates the amino acid uptake by body cells.
Working of Insulin
{GS3 – Envi – CC} Supreme Court ruling on Climate change
- Context (IE): The Supreme Court made an important ruling regarding climate litigation in India.
- It stated that people have a fundamental right to be free from adverse impacts of climate change. This right is derived from the right to life and the right to equality guaranteed in the IC.
- The Court articulated this new right in a case related to the conservation of the Great Indian Bustard, where climate change was only incidental to the arguments.
Increasing Climate litigations
- Governments and corporations are not doing enough to address climate change, leading more people to seek justice through legal channels.
- The Global Climate Litigation Report for 2023 found 2,180 climate-related cases in 65 countries.
- Most cases are filed in developed countries like the USA and Europe, which account for about 70% of all cases. However, there is a growing trend of climate-related cases in developing countries, including India.
- The report identified 11 cases in India, ranking it 14th among countries with the highest number of climate-related cases. Many of these cases use a rights-based approach similar to the one discussed by the Supreme Court.
- Petitioners often cite rights such as the right to life, human rights, and rights to health, food, water, or family life to advocate for stronger climate action.
Way forward
- These judgments could increase accountability in government & corporate actions on climate change. However, it’s unlikely that the verdicts alone will significantly reduce overall threat of climate change.
- While courts can effectively address issues like pollution and habitat protection, tackling climate change is more complex.
- Climate change requires multi-dimensional solutions beyond the capacity of individual governments.
- Courts may require the government to consider mitigation or adaptation plans but are unlikely to enforce such directives strictly.
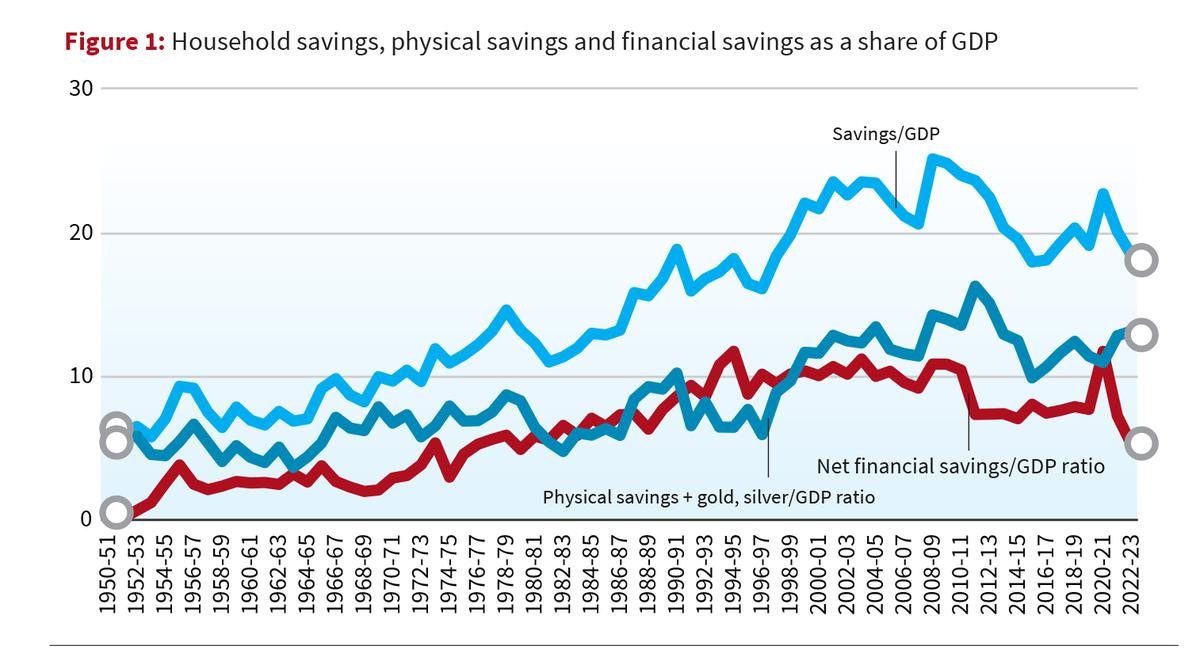
{GS3 – IE – Resources} Declining Household Savings
- Context (TH): Recent discussions in India have focused on the decline in household savings.
- This decline is mainly due to a significant drop in net financial savings, resulting in the household net financial savings to GDP ratio reaching its lowest point in forty years.
|
Reasons for decline in household net financial savings
- First, households may finance increased consumption by borrowing more or using up their financial savings. This increased consumption expenditure, despite the same level of disposable income, stimulates aggregate demand and output.
- The second factor contributing to a decrease in household net financial savings involves financing higher tangible (physical) investments by borrowing more or using up financial savings. This reduction in net financial savings stimulates aggregate demand and output through increased investment.
- Thirdly, if households face increased interest payments due to higher interest rates, they may cover the extra cost by borrowing more or depleting financial savings, resulting in decreased net financial savings.
- An analysis shows that the third factor (interest payments by borrowing) played a major role in the decline of household net financial savings.
|
Impacts of High debt burden
- The increase in household debt burden raises two macroeconomic concerns.
Concerns over debt repayment and financial vulnerability
- Debt sustainability depends on the household’s ability to repay, which is determined by the income flow.
- When households struggle to meet debt repayments, the income of the financial sector is reduced. This impacts the financial sector’s balance sheets, potentially affecting the macroeconomy.
- If the financial sector responds by reducing credit disbursement to the non-financial sector, it can have cascading effects on the economy.
Impact on consumption demand
- Apart from disposable income, household consumption can be influenced by wealth, debt, and interest rates. Reduced household wealth may lead to lower consumption as households aim to preserve their wealth by increasing savings.
- Higher household debt can also decrease consumption in two ways.
- Firstly, if increased leverage suggests higher default risk, banks may reduce credit disbursement, affecting consumption.
- Secondly, higher debt increases the interest burden, along with the impact of higher interest rates on consumption.
{GS3 – S&T – AI} Bitcoin Halving
- Context (LM | TOI): Bitcoin, the top cryptocurrency globally, experienced a planned decrease in its new coin creation rate on April 19. This event is called a “Bitcoin halving“.
- After the halving, Bitcoin’s price stayed relatively steady, with a small decrease of 0.47% to reach ₹58,89,117 on Wazirx.
- Bitcoin’s creator, Satoshi Nakamoto, set a limit of 21 million coins for its total supply.
Bitcoin mining
- Bitcoin mining is the process by which transactions are officially entered on the blockchain. It is also the way new bitcoins are launched into circulation.
- Mining is conducted by miners using hardware and software to generate a cryptographic number that is equal to or less than a number set by the Bitcoin network’s difficulty algorithm.
- The first miner to find the solution to the problem receives bitcoins as a reward, and the process begins again. So, in reality, miners are essentially getting paid for their work as auditors.
Bitcoin halving
- A Bitcoin halving occurs approximately every four years.
- It is an event where the reward for mining Bitcoin transactions is cut in half.
- In other words, the number of new bitcoins created and awarded to miners is reduced by 50%.
- The halving is hard-coded into Bitcoin’s protocol and is a fundamental part of its monetary policy.
Learn more on Bitcon Halving.
{GS3 – S&T – Defence} India delivered BrahMos to Philippines
- Context (IE): India delivered the BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles to the Philippines as part of a $375-million deal signed in 2022.
- India’s first major export order is for a shore-based variant of an anti-ship cruise missile.
- The missile, with a range of approximately 290 km, is produced by BrahMos Aerospace.
- BrahMos Aerospace is a joint venture between India’s DRDO and Russia’s NPO Mashinostroyeniya.
- The supersonic cruise missile is already operational in all three branches of the Indian armed forces.
- BrahMos NG, a smaller and lighter next-generation version, is set for trials in the first half of 2024.
- Efforts are underway to upgrade existing BrahMos missiles to extend their range to 500 km for land attacks and 400 km for ship attacks.
{GS3 – S&T – Space} Insurance strategy for India’s space sector
- Context (TH): A Research Fellow at Spaceport SARABHAI emphasised the urgent need for a comprehensive insurance strategy for India’s space sector.
- He authored a report titled “Financial Risk Coverage of India’s Commercial Space Launch Industry: Need for Developing Insurance and Reinsurance Capabilities.”
- The report highlights the importance of regulatory clarity, financial market development, and industry alignment for the success of India’s space sector.
- It analyses existing space laws globally and compares them to identify best practices for risk governance.
- Spaceport SARABHAI, a space think tank based in Bengaluru, released the report on Friday.
Suggestions from the report
- India’s Space Policy of 2023 aims to promote commercial space presence but lacks comprehensive coverage of space insurance and liability.
- States typically adopt two approaches to address insurance issues.
- Regulating insurance obligations in legislation.
- Leaving specifics to be mentioned in licenses.
- Both approaches require licensees or operators to obtain insurance policies, creating a stable regulatory environment.
- However, the report suggests India should ideally adopt the first approach, which outlines insurance obligations in legislation.
Reason
- By outlining insurance obligations in national legislation, the state clearly expects the private sector to meet those obligations. This gives private sector entities certainty about their liability obligations, which are enforceable by law.
- India’s historical experience with bureaucratic red tape, i.e. ‘license-raj’. Allowing government officials to devise specific liability & insurance conditions for each license could lead to excessive and rigid rules.
- Adopting the first approach would help avoid such bureaucratic hurdles and provide clarity and consistency in the regulatory environment.
{Prelims – In News} Earth Day
- Context (LM): Earth Day is marked across the globe on April 22 to support environmental conservation efforts.
- Theme 2024: ‘Planet vs. Plastics’.
- Started on US college campuses in 1970 after a massive oil spill in Santa Barbara.
- Initiated by US Senator Gaylord Nelson to generate student and public consciousness about air and water pollution.
- The date was chosen based on the college calendar to maximise participation.
- The Paris Climate Agreement was also symbolically signed on the same day in 2016.
|
{Prelims – In News} Ethylene Oxide
- Context (TOI): International agency identified cancer-causing chemicals, ethylene oxide, in Indian spices.
- Ethylene oxide (EtO), also known as Oxirane, is a colorless, flammable gas with a sweet odor. It is used primarily to produce other chemicals, including antifreeze.
- Besides being produced from natural sources, it can also be generated from water-logged soil, manure, and sewage sludge.
- It can be used as a fumigant to control fungi and bacteria growth in dry food products (e.g. seeds, herbs and spices).
- The ability of ethylene oxide to damage DNA makes it an effective sterilizing agent but also accounts for its cancer-causing activity.
- The use of plant protection products containing ethylene oxide is prohibited in the EU as it is classed as a Category 2 carcinogen and mutagen.
- Short-term exposure to the carcinogen can affect the human central nervous system, and cause depression and irritation of the eyes and mucous membranes.
- Prolonged exposure can irritate the eyes, skin, nose, throat, and lungs, and damage the brain and nervous system.
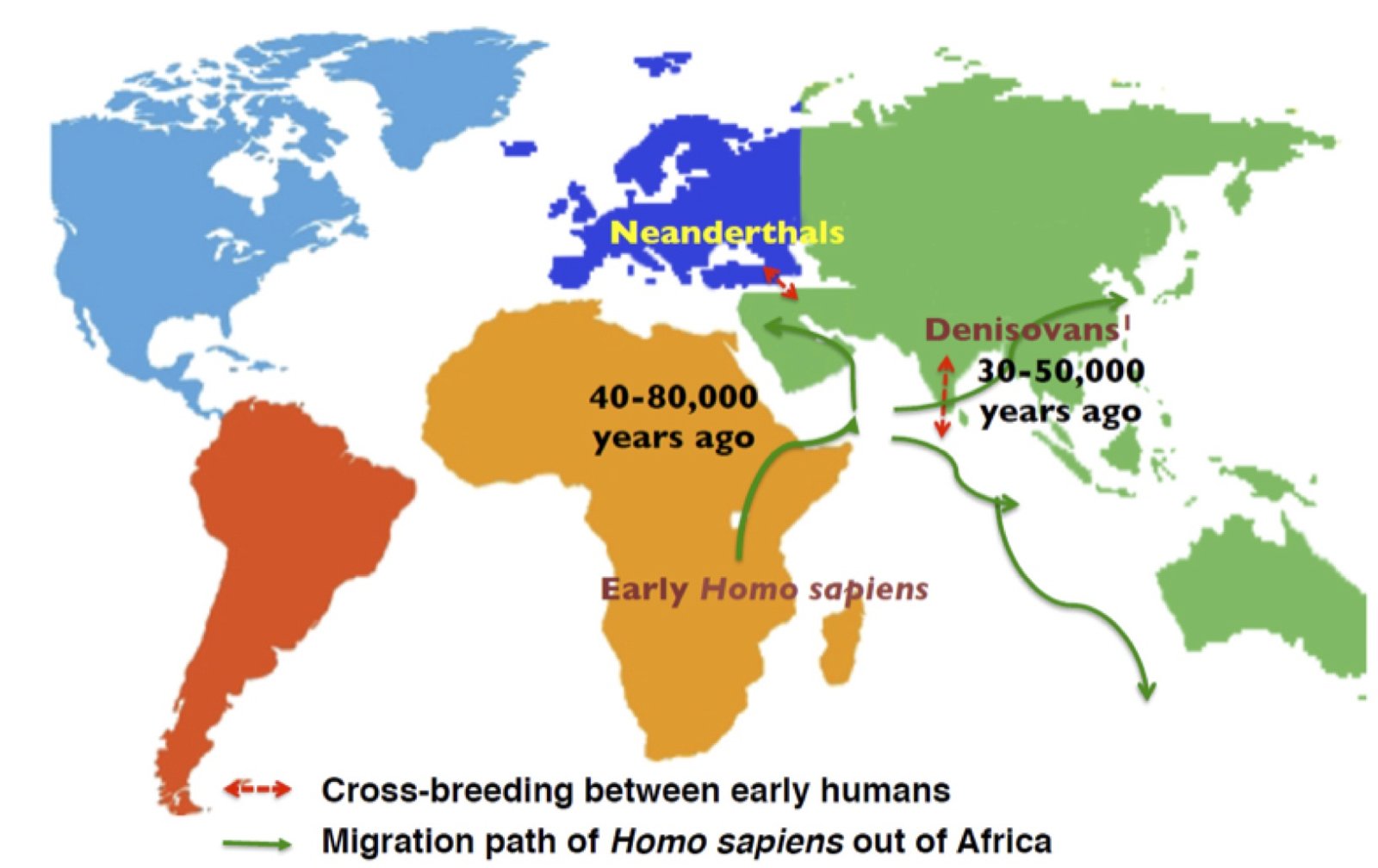
{Prelims – In News} Neanderthals and Denisovans
- Context (DTE): As per Scientists, Indians derive 1-2% of their ancestry from gene flow from Neanderthals and Denisovans.
Neanderthals
- The Neanderthals were likely our closest human relatives. Members of this now-extinct group were hominins — a lineage that includes living humans (Homo sapiens) and our extinct relatives.
- The first fossils to be called Neanderthals were found in 1856 in Germany, at a site in the Neander Valley (where Neanderthals get their name from).
- The German word for valley is ‘Tal’ although in the 1800s it was spelt ‘Thal’. Homo neanderthalensis therefore means ‘Human from the Neander Valley’.
- Neanderthals diverged from modern humans around 500,000 years ago, likely evolving outside of Africa.
Distribution
- Remains of this species have been found scattered across Europe and the Middle East.
- The eastern-most occurrence of a Neanderthal may be represented by a fossil skull from China known as ‘Maba’.
Physical Features
- Neanderthals were generally shorter and had more robust skeletons and muscular bodies than modern humans.
- Males averaged about 168 centimetres in height while females were slightly shorter at 156 centimetres.
- Neanderthals had a long, low skull (compared to the more globular skull of modern humans) with a characteristic prominent brow ridge above their eyes.
- Their heads were long rather than globe-shaped and had lower foreheads and crowns.
Tools
- Like early humas, Neanderthals, made an assortment of sophisticated tools from stone and bones. These included small blades, hand axe and scrapers used to remove flesh and fat from animal skin.
Denisovan
- The Denisovans, together with the Neanderthals, are the closest extinct relatives of modern humans.
- The Denisovans are named for the location where the first fossils were found, Denisova Cave in the Altai Mountains of Siberia, Russia.
{Prelims – In News} New Oral Vaccine for Cholera: Euvichol-S
- Context (FE): WHO prequalifies new oral vaccine for cholera, Euvichol-S.
- The new vaccine is the third product of the same family of vaccines for cholera in the WHO prequalification list, Euvichol and Euvichol-Plus.
- Euvichol-S is a simplified formulation of the oral cholera vaccine (OCV) Euvichol-Plus.
- The vaccine is manufactured by South Korea-based EuBiologics Co., Ltd. (EuBiologics is the largest supplier of oral cholera vaccine in the world, representing more than 80% market share).
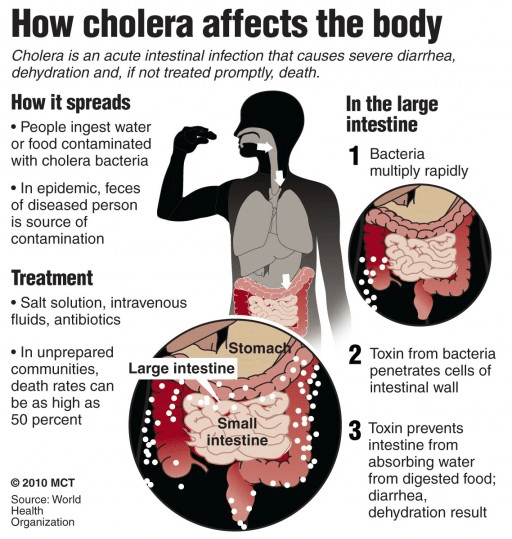
Cholera
- Cholera is an acute, diarrheal illness caused by infection of the intestine with the toxigenic bacterium Vibrio cholerae.
- The cholera bacterium is usually found in water or in foods that have been contaminated by feces from a person infected with cholera bacteria.
- Spread: It is most likely to occur and spread in places with inadequate water treatment, poor sanitation, and inadequate hygiene.
- Symptoms: Rapid heart rate, loss of skin elasticity (the ability to return to original position quickly if pinched), dry mucous membranes, low blood pressure, thirst, muscle cramps.
{Prelims – S&T – Defence} Exercise Poorvi Lehar
- Context (PIB): Exercise Poorvi Lehar took place on the East Coast.
- It aimed to assess the Indian Navy’s readiness to tackle maritime security challenges in the region.
- The exercise involved participation from ships, submarines, aircraft, and special forces.
- It consisted of multiple phases, including combat training and firings to demonstrate the Navy’s capability to deliver ordnance accurately.
- Aircraft operated from various locations to maintain continuous Maritime Domain Awareness.
|





![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)