Current Affairs for UPSC Civil Services Exam – April 30, 2024
Subscribers of "Current Affairs" course can Download Daily Current Affairs in PDF/DOC
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
{GS2 – IR – Asia} Sierra Madre | South China Sea
- Context (IE): China has demanded the removal of the Sierra Madre ship. Philippines has rejected it.
About the Sierra Madre
- Sierra Madre was constructed in the US for World War II and commissioned in 1944 as a landing ship.
- Subsequently, it was sent to Vietnam during the US participation in the Vietnam War (1954-75).
- In 1976, it was transferred to the Philippines, an ally of the US.
- In the 1990s, the Philippines decided to bring this ship to the Second Thomas Shoal, a submerged reef located in the South China Sea.
- In 1999, the Sierra Madre was left on the Second Thomas Shoal, which is a part of the mostly uninhabited Spratly Islands in the South China Sea.
- The placement of the ship was deliberate in order to further its territorial claims.
- China also has deployed its ships in the vicinity. It has also directed water cannons at supply boats.
- The ship is largely dilapidated and rusting. However, for the Philippines, its removal would risk weakening its claims over the islands and the Chinese presence being established.
|
Confrontation over the Spratly Islands
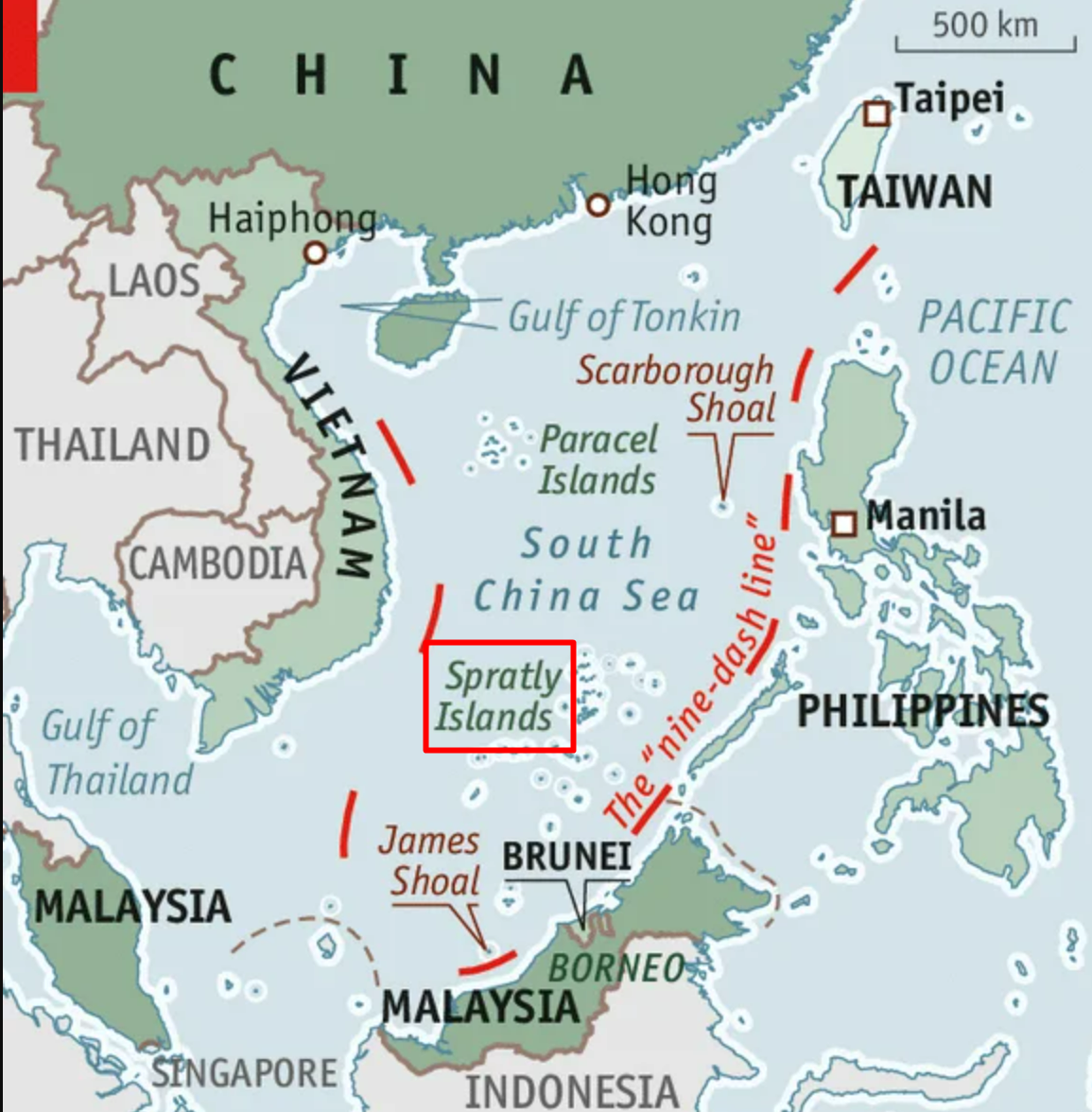
- For decades, countries in the region have extended overlapping claims on the South China Sea, claiming ownership over the Spratly Islands and the Paracel Islands.
- Along with issues over sovereignty, the rich oil and gas reserves in the region and its rich fishing waters have also encouraged countries to lay their claims.
- China took effective control of the disputed Scarborough Shoal after a tense standoff in 2012.
- In the Xi Jinping regime, China has assumed a hardened stance, claiming 90% of the South China Sea.
- China also rejected the 2016 International Court of Justice ruling regarding the South China Sea.
US response on the issue
- The US supports the Philippines as an important strategic ally.
- In May 2023, the two countries also agreed on new guidelines for a defence treaty from 1951.
- The guidelines reaffirm the invoking mutual defence commitments under the 1951 U.S.-Philippines Mutual Defense Treaty in case of any aggression.
India’s stakes in South China sea
- Freedom of navigation: The South China Sea is not China’s sea but a global common. India supports freedom of navigation and the rule of law across global commons.
- Sea Lane of Communication: It has been an important sea lane of communication since the very beginning, and passage has been unimpeded over the centuries.
- History of Indian presence: Indians have sailed these waters for well over 1,500 years, and there is ample historical and archaeological proof of a continuous Indian presence from Malaysia to China.
- Trade route: Nearly $200 billion of our trade passes through the South China Sea.
- Essential for regional peace: India shares the stakes in the peace and security of this region, which are essential for our economic well-being.
- Support to Philipines: India has reiterated support for Philippines in upholding its national sovereignty.
{GS2 – IR – Groupings} Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI)
- Context (HT): The 6th edition of the International Conference on Disaster Resilient Infrastructure was held in New Delhi.
- Theme: ‘Investing today for a more resilient tomorrow.’
- Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) was established in 2019 at the UN Climate Action Summit under India’s leadership and with the support of the UN Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR).
- It is a multi-stakeholder global coalition of nations, UN organisations, multilateral development banks, corporate sector, and academic institutions.
- Objective: It aims to promote the resilience of infrastructure systems to climate and disaster risks.
- Members: 39 countries and 7 organisations. Membership in the CDRI is open to all entities, subject to the approval of the governing council.
- The governing authority of the CDRI is divided into three groups: the Governing Council, the Executive Committee and the Secretariat.
- Secretariat: New Delhi, India
Initiatives by CDRI
- Infrastructure Resilience Academic eXchange (IRAX): It bridges the talent gap for building disaster-resilient infrastructure.
- Infrastructure for Resilient Island States: To strengthen critical infrastructure in Small Island Developing States (SIDS).
- CDRI WORLD knowledge portal: It acts as a central repository for resources, tools, and best practices related to disaster-resilient infrastructure.
- Infrastructure Resilience Accelerator Fund (IRAF): Provides support to developing & small island nations.
- CDRI Technical Resource Handbook: It provides practical guidance on assessing infrastructure vulnerabilities and implementing resilience measures
- DRI Connect: It is a one-stop online space for DRI stakeholders to connect, learn and collaborate towards improved practices, processes and policies for resilient infrastructure systems.
{GS2 – Polity – IC – Elections} Winning Elections Without Any Opposition
- Context (TH): The ruling party’s candidate from the Surat Lok Sabha constituency in Gujarat has been declared elected unopposed.
- Since 1951, at least 35 candidates have been elected unopposed to the Lok Sabha.
- The majority of them were in the first two decades after independence, with the last being in 2012.
Law related to the declaration of the results in unopposed elections.
- Rule 11 of the Conduct of Election Rules 1961 permits the Returning Officer (RO) to publish a list of contesting candidates and the declaration of results in an uncontested election
- Section 53 (3) of the Representation of the People Act (RPA), 1951, deals with the procedure in uncontested elections.
- If the number of such candidates is less than the number of seats to be filled, the RO shall forthwith declare all such candidates to be elected.
- It is important to note that the actions of the RO in this regard are guided by Section 33 of the Act.
- Section 33 of the RPA: This section deals explicitly with the presentation of nomination papers and the requirements for a valid nomination.
Returning Officers (ROs)
|
Handbook for Returning Officers issued by the Election Commission
- If only one candidate contests in any constituency, that candidate should be declared to have been duly elected immediately after the last hour for withdrawal of candidature.
Conditions under which a Candidate is declared Elected Unopposed
- If only one candidate is contesting in any constituency.
- When all other candidates withdraw their nominations or are disqualified, leaving only one candidate in the running.
Issues with Unopposed Election of Candidates
Concerns for NOTA Voters
- This process does not allow electors to exercise the None of the Above (NOTA) option (Negative Voting).
Negative Voting
|
Undermining the Relevance of Voters
- The present electoral process, in a sense, excludes the ”electors” entirely from the election process and denies their rights if there are no candidates to contest.
- The democratic process is fulfilled only when there is interest among the contestants and the voters.
- A person not having even a single vote would legislate on behalf of the entire constituency.
Ambiguous Provision Under Section 65, RP Act, 1951
- A complete boycott of elections will be treated as everyone receiving zero votes and covered under Section 65, which deals with ‘Equality of votes’.
- If the votes are equal, the addition of one vote will entitle any of those candidates to be declared elected.
- The RO shall forthwith decide between those candidates by lot and proceed as if the candidate on whom the lot falls had received an additional vote.
- The will of the people is replaced by the system’s practicality in identifying who will represent the people when they did not participate in the process.
- The RPA, 1951, provides for issuing another notification if no candidates file their nomination the first time but is silent if the same thing is repeated after that.
- This means Candidates can nullify the process, but people collectively cannot.
Learnings from the General Financial Rules (GFRs)
|
Law for Nomination in India
Section 33 of RPA, 1951
- Section 33 of the RPA, 1951 contains the requirements for a valid nomination.
- As per the RP Act, an elector above 25 years of age can contest the Lok Sabha election from any constituency in India if they are an elector from any of the constituencies.
- A candidate can file up to four nomination papers with different sets of proposers.
Proposers for Recognised Political Parties
- However, the candidate’s proposer(s) should be an elector(s) from the respective constituency where the nomination is being filed.
- In the case of a recognised party (national or State), the candidate needs to have one proposer.
Proposers for Unrecognised Political Parties
- Candidates set up by unrecognised parties and independents need to be subscribed by ten proposers.
Scrutiny of Nomination Papers
- Section 36 of the RP Act sets out the law regarding the scrutiny of nomination papers by the RO.
- It provides that the RO shall not reject any nomination for a defect that is not substantial.
- However, it specifies that the signature of the candidate or proposer found not genuine is grounds for rejection.
Recourses Available Against Rejection of Nomination Papers
Exploring Election Tribunal Options
- RP Act, 1951 establishes Election Tribunals to resolve such disputes and Section 100 of the RPA outlines the grounds for declaring a candidate’s election void.
- Parties dissatisfied with the Election Tribunal’s decision can appeal to the HC and ultimately to the SC.
Article 329 Read With RP Act, 1951
- Article 329(b) of the IC, read with the RP Act, 1951, provides that no election shall be called into question except by an election petition before the concerned HC.
- Improper rejection of nomination papers is one of the grounds on which such an election petition can be filed.
- The RP Act provides that HCs shall endeavour to conclude such trials within six months, which has mostly not been followed in the past.
- Speedy disposal of election petitions would be a step in the right direction.
Moving to the Supreme Court
- The aggrieved party can file an appeal to the SC within 30 days of the HC’s order.
- SC in Jagan Nath v. Jaswant Singh, 1954: The burden of proving that corrupt practices have significantly impacted a candidate’s election lies with the petitioner.
- The court also clarified that an election petition’s scope is confined to the grounds outlined in Section 100 of the RP Act, 1951.
- SC in Mohinder Singh Gill v. Chief Election Commissioner (1978): Elections must be conducted fairly, and any violation of this principle would nullify the election.
- Election tribunal can investigate allegations of corrupt practices, even if not explicitly raised in the election petition.
Amending the First-Past-the-Post-System (FPTPS)
- Introducing a minimum percentage of votes for the winning candidates to be declared must be considered.
- If no candidate offers herself for elections, that seat should be transferred to the nominated category, where the President can appoint a person as per prescribed qualifications without consulting the GOI.
Article 329 of IC and Bar on Interference by Courts in Electoral Matters
Trial of Election Petition – Section 86 of RP Act, 1951
|
{GS3 – Envi – CC} Warming of Indian Ocean
- Context (TH): According to an analysis led by scientists at the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune, the warming of the Indian Ocean will accelerate.
Important Findings
- The Indian Ocean is warming, with a 1.2°C increase from 1950 to 2020. Climate models predict further warming of 1.7°C to 3.8°C from 2020 to 2100.
- Marine heatwaves in the Indian Ocean may increase tenfold, from 20 days annually to 220-250 days, linked to cyclone formation.
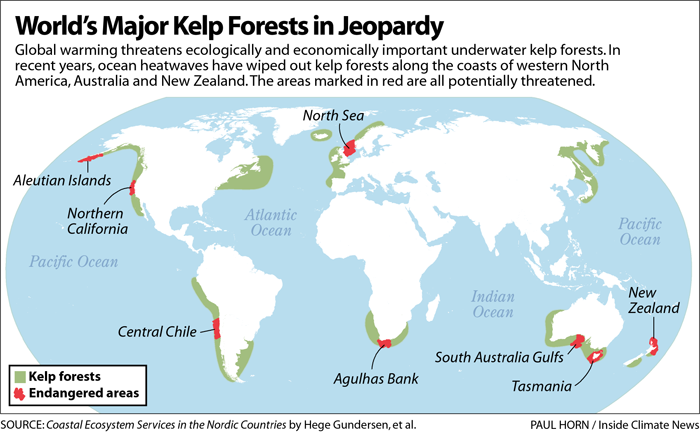
- The tropical Indian Ocean could experience near-permanent heatwave conditions, which could accelerate coral bleaching, seagrass destruction, and kelp forest loss. These changes will negatively affect the fisheries sector.
- Rising heat content leads to sea-level rise through water’s thermal expansion, responsible for over half of the sea-level rise in the Indian Ocean.
- Changes in the Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) are expected, impacting the monsoon.
- Global warming is the primary cause of these changes.
{GS3 – IE – Banking} RBI sets criteria for SFBs aiming to become Universal Banks
- Context (IE): The RBI stated that small finance banks (SFBs) must have a minimum net worth of Rs 1,000 crore to become universal banks under on-tap licensing norms.
Other criteria for SFBs to become a universal bank
- Must have scheduled status and a five-year satisfactory performance track record.
- Their shares must be listed on a recognised stock exchange.
- They should have posted a net profit in the last two financial years.
- They should have gross non-performing assets (GNPA) ≤3% and net non-performing assets (NNPA) ≤1%, respectively, in the last two financial years.
- There’s no mandatory requirement for an eligible SFB to have an identified promoter, but existing promoters must continue.
- Any dilution plan for promoter shareholding already approved by the RBI should not change.
- SFBs with diversified loan portfolios are preferred by the RBI.
{GS3 – IE – Banking} RBI’s Guidelines for Asset Reconstruction Companies
- Context (BS): The RBI recently issued a master direction for asset reconstruction companies (ARCs). The guidelines will come into effect from April 24, 2024.
Guidelines given to ARCs
- ARC must have a minimum net owned fund (NOF) of ₹300 crore by March 31, 2026. Non-compliant ARCs would face supervisory action, including a ban on new business until they meet the required minimum NOF.
- ARCs with a minimum NOF of Rs 1000 crore can act as resolution applicants.
- An ARC may deploy any surplus funds available with it in government securities, deposits with scheduled commercial banks, SIDBI, NABARD, or other specified entities.
- They can also invest in short-term instruments like money market mutual funds, certificates of deposit, and corporate bonds/commercial papers.
- Short-term investments must have a rating of AA- or above by an eligible credit rating agency.
- Maximum investment in such short-term instruments is capped at 10% of the NOF.
{GS3 – IE – Industry} Corporate Governance Charter for Startups
- Context (TH): The Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) has come up with a Corporate Governance Charter for startups to serve as a self-governing code for them in their compliance journey.
- The Charter is intended to be used by startups as a “ready reckoner” as they glide along the path of good governance.
- The guidance will be organised into four distinct stages: inception, progression, growth, and going public. Each stage will highlight specific governance principles requiring extra attention at that phase.
- Objective: To help start-ups become responsible corporate citizens and also enable them to share this with their stakeholders to establish themselves as being well-governed.
- Significance: It allows startups to measure their governance progress, with score changes indicating improvements in governance practices as assessed against the scorecard from time to time.
Confederation of Indian Industry (CII)
|
What is Corporate Governance?
- Corporate Governance refers to the set of rules, practices, and processes that guide how a company is controlled and managed.
- Objective: To ensure that a company operates in a responsible, transparent, and ethical manner while maximising value for its shareholders.
For detailed explanation on Startups >PMF IAS November 2023 Monthly Magazine.
{GS3 – IE – SEBI} Anchor Investors
- Context (BS): Vodafone Idea (Vi) allocated 4.9 billion shares to anchor investors before its follow-on public offer (FPO).
Anchor Investors or Cornerstone Investors (as they are called globally)
- They are institutional investors like sovereign wealth funds, mutual funds and pension funds.
- They are invited to subscribe to shares before Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) or FPOs open. Their participation aims to boost the issue’s popularity.
- Anchor investors commit to purchasing shares at a predetermined price. Each anchor investor must invest a minimum of ₹10 crores in the issue.
- The benefit for institutional investors applying in anchor quota is that they get guaranteed allotment.
- They cannot sell their shares for 30 days from the date of allotment, as opposed to IPO investors, who are allowed to sell on listing day.
- Anchor investors were introduced by the Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI) in 2009.
{GS3 – S&T – Defence} Hangor class vs India’s Kalavari Class Submarines
- Context (IE): China recently launched the first Hangor class submarine for Pakistan.
About Hangor Class Submarine
- The Hangor class is derived from the Chinese Type 039A Yuan class.
- It is a diesel-electric attack submarine named after the decommissioned PNS Hangor, which sank the Indian frigate INS Khukri during the 1971 war.
- The submarine has a battery for underwater operation, charged by the diesel engine.
- It features four diesel engines and an air-independent propulsion (AIP) system.
- Significance of AIP system: Conventional diesel-electric submarines must surface to recharge batteries every 2-5 days. This surfacing makes them detectable by enemy radar and exhaust fumes sensors. AIP systems can increase underwater endurance to over 15-20 days.
- Attack submarines like the Hangor class sink other vessels using torpedoes or cruise missiles.
- It has six 21-inch torpedo tubes and can launch anti-ship missiles.
- It is also equipped with the Babur-3 subsonic cruise missile with a range of 450 km.
Comparison with India’s Kalavari Class Submarines
- Kalavari class is based on the French Scorpene class. India operates six Kalavari class submarines, and three more are expected by the 2030s. Kalavari carries six German torpedoes and French Exocet missiles.
- Both have a top speed of 20 knots and use diesel-electric propulsion.
- The hangor class has built-in AIP. The Indian Navy is installing indigenous AIP on Kalavari.
- Neither has vertical launch systems like India’s Arihant class. Vertical launch enables carrying larger Brahmos-NG missiles.
{GS3 – S&T – Space} Sympathetic Solar Flares
- Context (TOI): The Sun has exhibited a “super” explosion, characterised by the simultaneous eruption of four solar flares.
Quadruple solar flare incident
- The quadruple solar flares erupted from separate regions across the Sun’s surface.
- Each of these originated from different sunspots and a large magnetic filament—a loop of plasma suspended above the solar surface.
- The blast sites were spaced very far, yet the flares were part of a single, interconnected eruption known as a Sympathetic solar flare.
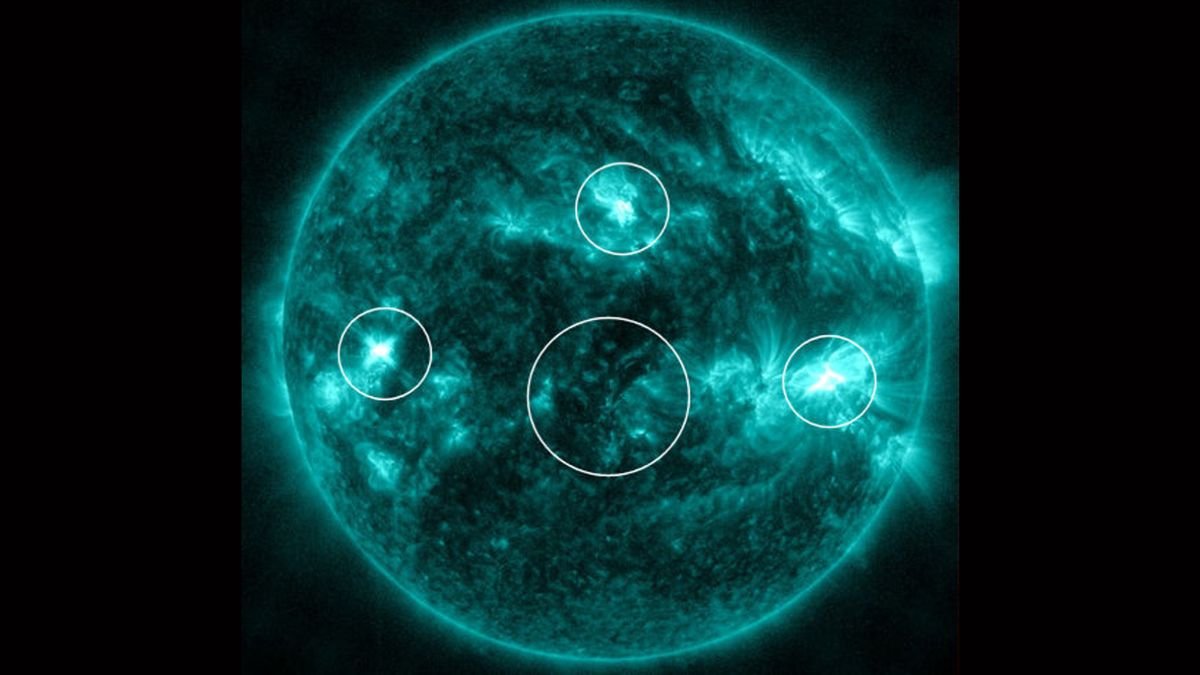
- This type of solar outburst occurs when sunspots or filaments are invisibly linked by massive magnetic field loops that arch above the solar surface, resulting in successive outbursts.
- Sympathetic solar flares typically involve just two linked flares, varying in intensity from minor outbursts to X-class flares, the most powerful class of solar flares.
- Recent outbursts had twice as many flares, earning it the designation of a “super-sympathetic” flare.
- The concurrent blasts covered approximately a third of the solar surface facing Earth.
- One of the flares may have launched a solar storm toward Earth.
- Subsequent Coronal Mass Ejections and their potential trajectory toward Earth are yet to be confirmed.
{Prelims – In News} Authorised Economic Operator (AEO) Status
- Context (TH): The Centre has extended Authorised Economic Operator (AEO) status to the gem and jewellery sector.
- The AEO is a programme under the World Customs Organisation (WCO) SAFE Framework of Standards (SAFE FoS) to secure and facilitate global trade.
- The AEO program is one of the core parts of the second pillar (Customs to Business Partnership) of the SAFE FoS.
- Objective: To enhance international supply chain security and facilitate movement of legitimate goods.
- Under this programme, Customs approves an entity engaged in international trade as compliant with supply chain security standards and grants it AEO status.
- The AEO programme was introduced as a pilot project in 2011 by the Customs Department as part of a broader framework for ease of doing business.
- In India, the Directorate General of Inspection (DGICCE) has been designated as the nodal implementing agency for the AEO Programme.
- India’s AEO Programme is in sync with the commitments made under Article 7.7 of WTO Trade Facilitation Agreement (TFA).
- AEO is a voluntary compliance programme administered by the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC).
- Significance: It enables Indian Customs to enhance and streamline cargo security through close cooperation with the principal stakeholders of the international supply chain.
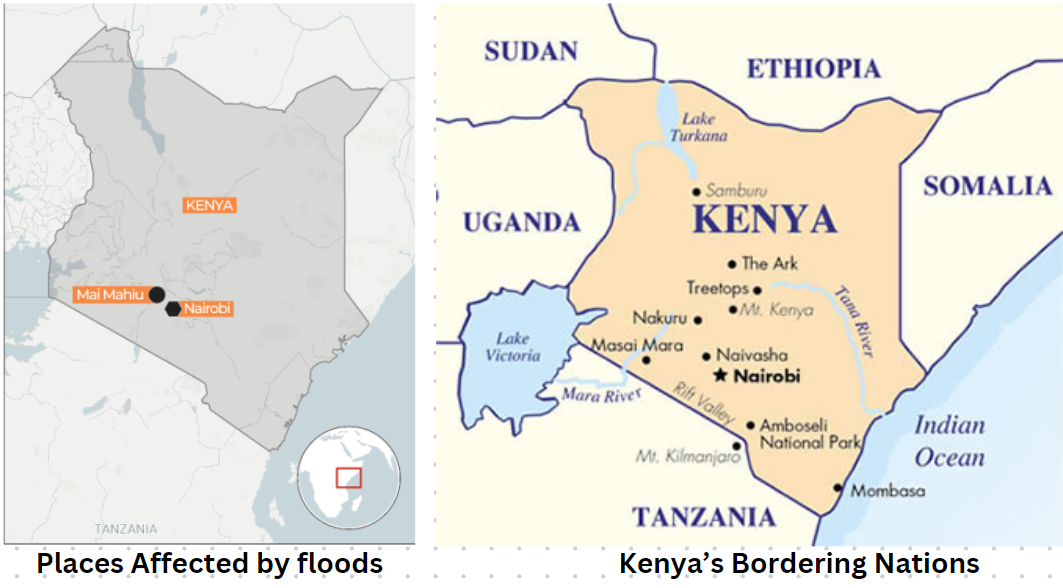
{Prelims – In News} Floods in Kenya
- Context (DTE): Old Kijabe Dam burst recently in southern Kenya, causing massive floods.
- Climate change and El Nino were blamed for the floods.
|
Another similar topic > Dubai Floods.
{Prelims – PIN World – Asia} River basins in Afghanistan
- Context (DTE): A study was carried out to map the river basins in Afghanistan.
- The researchers divided Afghanistan into five river basins.
- Harirod-Murghab River Basin (HMRB)
- Helmand River Basin (HRB)
- Kabul River Basin (KRB)
- Northern River Basin (NRB)
- Panj-Amu River Basin (PARB)
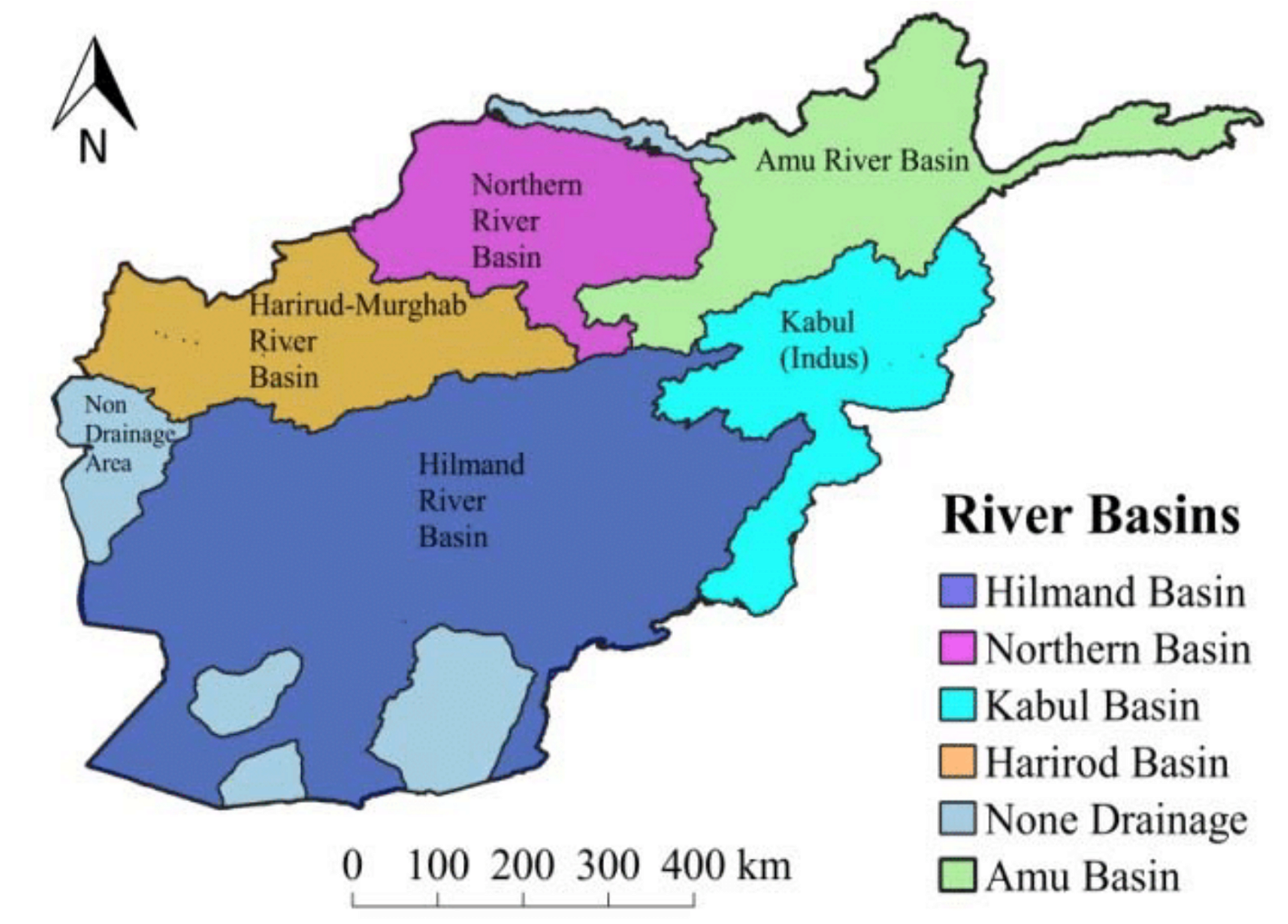
- Four are transboundary basins flowing to neighbouring countries except the Northern Basin.
Harirod-Murghab River Basin (HMRB)
- The Harirod and Murghab rivers form the drainage system in the north-western region.
- Origin and flow: Mountain range of central Afghanistan and flows westward across the Herat Valley.
- It is the main source of irrigation water for agriculture along the fertile lands of the valley.
Helmand River Basin (HRB)
- At 51 per cent, the HRB is the largest river basin in Afghanistan.
- The Helmand is the longest and biggest river in southwest Afghanistan.
- Origin and flow: Mountain ranges west of Kabul and drains into seasonal lakes along the Afghanistan-Iran border.
Kabul River Basin (KRB)
- KRB is mainly formed by the Kabul River.
- The Kabul River is the largest drainage system in the southeastern region.
- Origin and flow: Paghman Range and flows eastward to join the Indus River in Pakistan.
- The KRB covers 11 percent of Afghanistan. It receives water primarily from the Kunar River, which flows from melting glaciers and snow in the Hindu Kush mountains.
Northern River Basin (NRB)
- The Shirin, Sarepul and Balkh are the large rivers in the NRB.
- It supplies the least water among the five river basins.
Panj-Amu River Basin (PARB)
- The PARB is mainly formed by the Amu Darya, whose headstream is the Panj. Historically known as Oxus, the Amu Darya flows into Central Asia and ends in the now-dead Aral Sea.
- Origin and flow of Amu River: Glaciers of the Pamirs and drains to the northeastern and northern parts of Afghanistan.
- PARB is Afghanistan’s second-largest basin. It also overlaps with neighbouring Tajikistan.
{Prelims – PIN} Raja Ravi Verma
- Context (TH): The first true copy of the painting Indulekha by legendary artist Raja Ravi Varma will be unveiled at the Kilimanoor Palace.
- It is believed that the famous painting ‘Reclining Lady’ by Ravi Varma was modelled on Indulekha.

- Raja Ravi Verma was an Indian painter and artist, born in 1848 in Killimanoor Village, twenty four miles from the town of Kottayam in Travancore State.
- He was one of the first Indian artists to use oil paints and to master the art of lithographic reproduction of his work.
- He was the first Indian to use Western techniques of perspective and composition and to adapt them to Indian subjects, styles, and themes.
- In 1904, Viceroy Lord Curzon, on behalf of the British King Emperor, bestowed upon Varma the Kaisar-i-Hind Gold Medal.
- Themes of his paintings: Puranas, the great Indian epics – Mahabharata and Ramayana, portraits of both Indians and British in India.
- His most famous works include Damayanti Talking to a Swan, Shakuntala Looking for Dushyanta, Nair Lady Adorning Her Hair, and Shantanu and Matsyagandha.
{Prelims – S&T – Defence} LSAM 20 (Yard 130)
- Context (PIB): Ammunition Cum Torpedo Cum Missile Barge, LSAM 20 (Yard 130) was recently launched.
- It was built by MSME Shipyard, M/s Suryadipta Projects Pvt Ltd, Thane for Indian Navy.
- Significance: It would provide impetus to operational commitments by facilitating Transportation, Embarkation and Disembarkation of articles/ ammunition to Ships alongside jetties and at outer harbour.








![PMF IAS Environment for UPSC 2022-23 [paperback] PMF IAS [Nov 30, 2021]…](https://pmfias.b-cdn.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/pmfiasenvironmentforupsc2022-23paperbackpmfiasnov302021.jpg)